Trust me – you know what a search engine is.
You might not know how they work, but you’ve used one before.
Google is the go-to example, but plenty of other websites provide search features for finding information. Understanding how they work and how to rank on them can give your business a big advantage in acquiring new customers.
Let’s take a closer look at how search engines work and what they use to evaluate content.

The Guide to Winning
More Business Online
Want customers to find you online? A website is not enough.
What is a search engine?
A search engine is a program that identifies items in a database relevant to a specific keyword or query. When a user submits a word or phrase, the search engine looks for results that match that term.
The most popular search engine is Google – 90% of searches are performed on Google, where over 8.5 billion searches are conducted daily.
Plenty of sites offer their own internal search engines that let users search for content within the website. One example is Yelp, where users can search for things like “best restaurants near me” and the search engine will produce top results in their area.
But whether it’s Google, Yelp, or any other search engine, ranking at the top of search results is good for your business. Not only does it get more eyes on your content, but it also improves your website’s authority in general. The higher your authority is, the more likely it is to rank for other keywords and phrases.
Now let’s dive a little deeper into how search engines work – specifically Google.
How does a search engine work?
Search engines use bots to “crawl,” or review URLs and find new web pages on the Internet. A URL is like an address for your website that search engines use to discover your web pages. For example, www.thryv.com/blog/search-engine is this page’s URL.
When a new page is discovered, this URL is “indexed,” or sent back to the search engine, along with a set of data points that help the search program determine how to organize and rank the URL.
If you want to see what your page looks like in Google’s eyes, you can add “cache:” before the URL in your search bar. For example, the URL below would return a cached version of the Thryv home page.

When a new search is performed, the search engine uses data points gathered from its URLs to determine which pages should be shown and in what order. Since the search engine is designed to produce the best results possible, it will look for content that matches the intent of the search query.
Let’s review a brief example:
- Crawl: Thryv publishes a blog post targeting the keyword “best small business software.” Google’s bots crawl that page and discover this new piece of content.
- Index: Google indexes the page along with a few data points. It reviews the content and considers the intent and authority of the web page.
- Serve Results: A user enters “best small business software” into Google. The search engine then serves that blog post, along with other relevant results, to this user.
A few important things here. First, not all search engines work the same. Google might show different results from Bing, which might also be different from DuckDuckGo. It all depends on the factors that the search engine uses to rank its results (we’ll get into those in a moment).
Second, paid search is different from organic, and includes sponsored ads that look like this one:

People are bidding to be in those positions – but that’s a blog post for another day. For now, let’s focus on organic search results.
Lastly, Google updates its index constantly. Even if you ranked for a keyword today, you might not be in the same spot tomorrow. You need to keep your content fresh and updated over time if you want to keep winning the highest spots on search result pages.
Fortunately, we’re here to help. Let’s review the key factors that Google and other search engines are evaluating your content for.

The Guide to Winning
More Business Online
Want customers to find you online? A website is not enough.
How does a search engine rank URLs?
Search engines use an algorithm to instantly rank pages relevant to a user’s search. These algorithms are updated and optimized over time, so they serve the best results to each user.
Google plays its cards close to its chest when it comes to ranking factors, but there are a few things we know that play a role in how it evaluates content.
- Keywords: Keywords are words or phrases used in search queries. If your content includes the same terms that users are searching for, you’ll be more likely to rank for those keywords. While you shouldn’t stuff your content with keywords, they should be included throughout your page.
- Freshness: There are approximately 175 websites created every minute. With new web pages popping up all the time, Google tends to favor content that was recently published. That doesn’t mean you should scrap old web pages if they stop producing traffic. Instead, update them to show that they’re still relevant to your audience.
- Intent: Since Google’s purpose is to serve relevant information, one of the most important ranking factors is intent. In other words, does your page do what the user needs it to do? If the user is just looking for information, then they might not be ready to buy your product – so that’s not the place to try to sell it to them. But, if they’re looking to buy, your landing pages should reflect what they’re looking for in an offer. A landing page is a web page that’s specifically designed to convert web visitors into leads or customers. They usually include a product offer and a form that users can fill out to provide their contact information.
- Engagement: Engagement extends to the webpage and your website. If Google feels your site is credible, you’re more likely to rank for keywords. This takes time to accomplish because you need to provide a track record of credible, high-quality content.
Some factors are specific to the user, which can affect search results. These include:
- Location: Where the user is searching from can make a huge impact on their search results. Going back to our Yelp example, if I searched for “best restaurants near me,” I would see businesses in the greater Boston area. However, if someone in Texas searched for the same term, they would see restaurants in their location, instead.
- Search History: What the user has searched for recently can also impact their search results. For example, if you visit the same blog every day, you’re more likely to see pages from that blog pop up on your search results page. That’s because the search engine knows you prefer that website’s content.
- Browser Settings/Privacy: If a user has turned on privacy settings and does not allow cookie tracking, that can influence search results. Tracking cookies are used to serve personalized results to each user, and if those cookies are blocked, then the search engine has less information for its results page.
- Language: Some websites are only offered in certain languages. Therefore, if your website doesn’t offer a version that’s compatible with the user’s search, it won’t rank for that keyword. This is why it’s important to publish different, localized versions of your site if you are operating internationally.
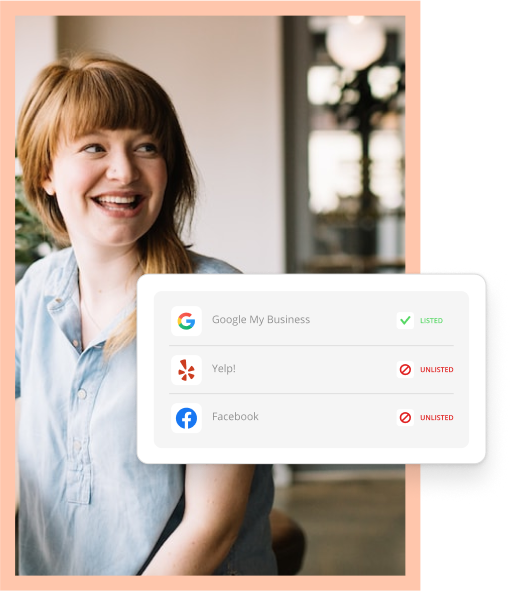
Pro Tip: You can use an online presence scanner to see how your business stacks up against the competition.
Searching for solutions?
Search engines are powerful tools that have revolutionized how we access information. For business owners, ranking at the top of search results leads to increases in site traffic and the opportunity to convert new visitors into valuable leads.
The challenge, however, is that search engines are updating their algorithms constantly, so keeping up with the latest news and trends is a battle for small businesses. Knowing how search engines work and what they want to serve users is an essential first step in staying ahead of your competition and winning keywords in organic search.